About the Holiday
First declared by the United Nations in 1999, World Space Week has grown to be the largest public space-related event in the world. The week is an international celebration of science and technology, and their contribution to the betterment of the human condition. This year’s theme is “Living in Space” and “explores humanity’s journey toward making space a habitat, emphasizing the innovative technologies, challenges, and collaborative efforts that make this vision a reality.” Looking to celebrate this initiative with more than 15,000 events in more than 90 countries, the week sponsors space education and outreach events held by space agencies, aerospace companies, schools, planetaria, museums, and astronomy clubs around the world. To learn more about the week, visit worldspaceweek.org.
Thank you to Simon & Schuster/Paula Wiseman Books and Barbara Fisch at Blue Slip Media for sending me a copy of this book for review.
Rock Star: How Ursula Marvin Mapped Moon Rocks and Meteorites
Written by Sandra Neil Wallace | Illustrated by Nancy Carpenter
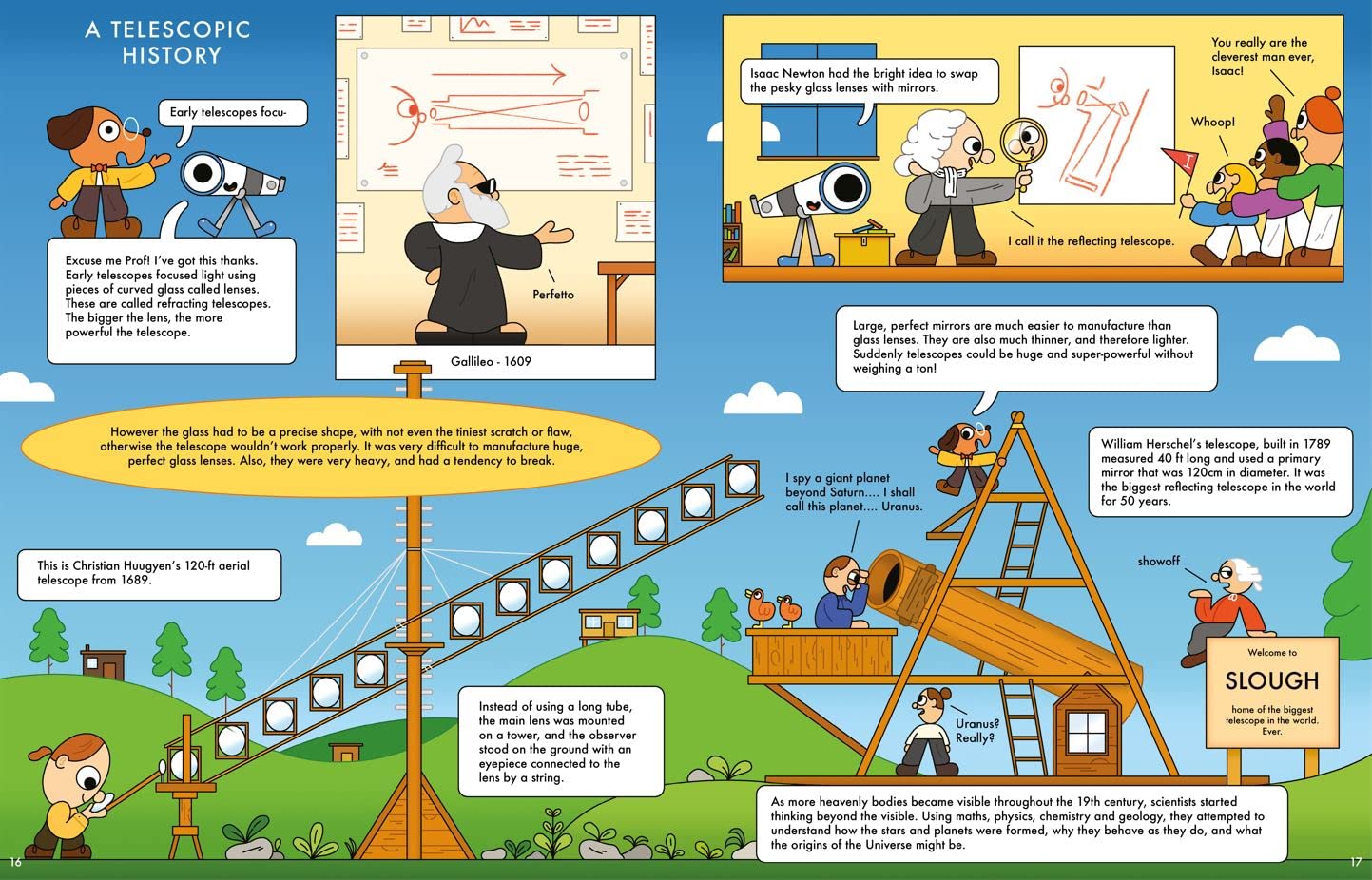
As a child growing up in Vermont, Ursula Marvin was captivated by the adventures winter brought. She was especially awed by the snowy mountains illuminated by “the frosty moonlight.” Her father was Vermont’s official entomologist, but Ursula had no intention of following in his footsteps or becoming any kind of scientist. She had her sights set on being an explorer. That was until she examined a rock under the microscope in college and decided to become a geologist. Her professor, however, denied her new major “because she was a woman.”

Illustration © 2025 Nancy Carpenter. Text © 2025 Sandra Neil Wallace. Courtesy of Simon & Schuster/Paula Wiseman Books.
Ursula took her talents to another university and earned a geology degree. She was an expert in recognizing rare minerals in Earth rocks and was tapped to be one of the first geologists to study rocks brought back from the moon. What she found was a world of color, minerals that proved “its surface was once a bubbling ocean of melted rock.” Ursula also studied meteorites, finding “minerals no one knew existed beyond Earth.” Her work revolutionized scientists’ views of the solar system.
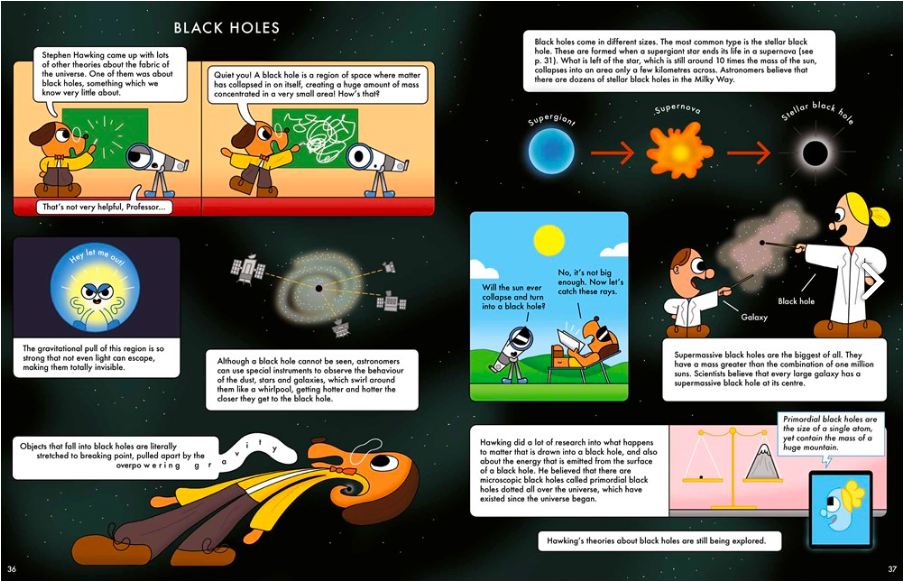
But Ursula still yearned to explore, in particular she wanted to be the first woman to find meteorites in Antarctica—the coldest place on Earth. She loaded up a bag with frigid-cold-weather gear and joined an expedition. When Ursula and her male teammates landed, they set up camp. They had to work fast because winter was on its way, threatening to bury any meteorites under ice and snow for another year.

Illustration © 2025 Nancy Carpenter. Text © 2025 Sandra Neil Wallace. Courtesy of Simon & Schuster/Paula Wiseman Books.
Ursula wondered if she’d be able to recognize meteorites under these conditions, but she needn’t have worried. On her first day, a rock caught her eye. Examining it, she discovered distinctive traits—she’d discovered her first meteorite! Ursula was in her element, thriving in the harsh weather and “collecting meteorites more than four billion years old.”
But not every day was a success. Ursula struggled to climb a mountain-like nunatak in her too-big boots, she mistook an ordinary Earth rock for a meteorite, and on the worst day, with one snowmobile broken, the team went exploring without her. Ursula vowed never to be left behind again.

Illustration © 2025 Nancy Carpenter. Text © 2025 Sandra Neil Wallace. Courtesy of Simon & Schuster/Paula Wiseman Books.
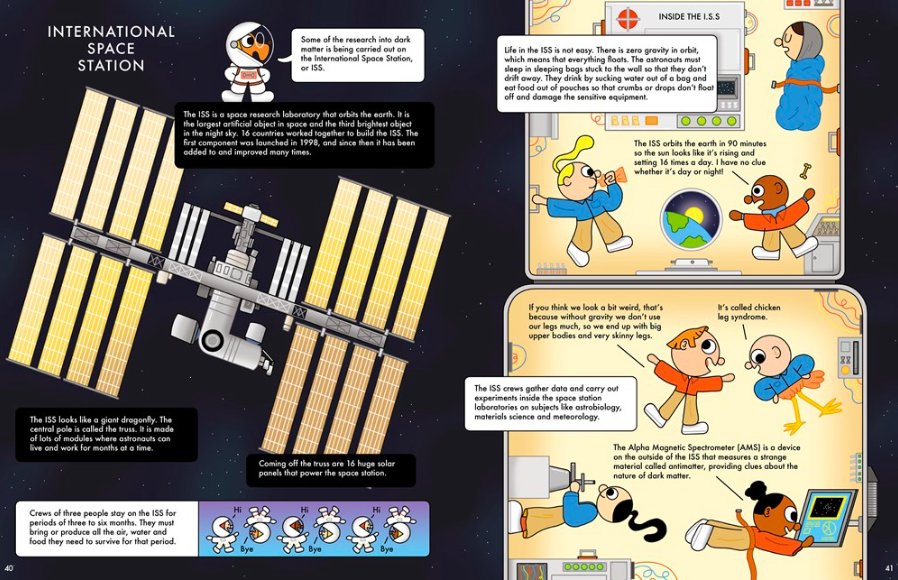
With only one week left in the expedition, Ursula rode across the ice to “unexplored places where the meteorites were bigger and rarer.” She wanted to be the one to find the last meteorite of the trip, to be the one to discover a meteorite from the moon. But a fall dashed those dreams as she was airlifted to the hospital, leaving her teammates to collect the final meteorite.

Illustration © 2025 Nancy Carpenter. Text © 2025 Sandra Neil Wallace. Courtesy of Simon & Schuster/Paula Wiseman Books.
Back at home, Ursula was excited to examine this small meteorite, which looked so different from the others. She recognized the world of color from her earlier studies. “Ursula’s teammates had discovered the first lunar meteorite on Earth without her.” Instead of feeling disappointed, she was “jubilant.” She went on to become a preeminent expert on this moon meteorite and others and to inspire women to become scientists, many exploring Antarctica, where they found more moon meteorites and even some from Mars more than four billion years old. Ursula’s influence can still be seen today in her work as well as in the Marvin Asteroid and Moon’s Marvin Crater named for her.
Extensive back matter following the story includes an Author’s Note about the astonishing life and influence of Ursula Marvin; quotations from Ursula’s Antarctica journals; facts about Antarctica; dated milestones of Ursula’s life, education, and work; resources; and two photographs.

Illustration © 2025 Nancy Carpenter. Text © 2025 Sandra Neil Wallace. Courtesy of Simon & Schuster/Paula Wiseman Books.
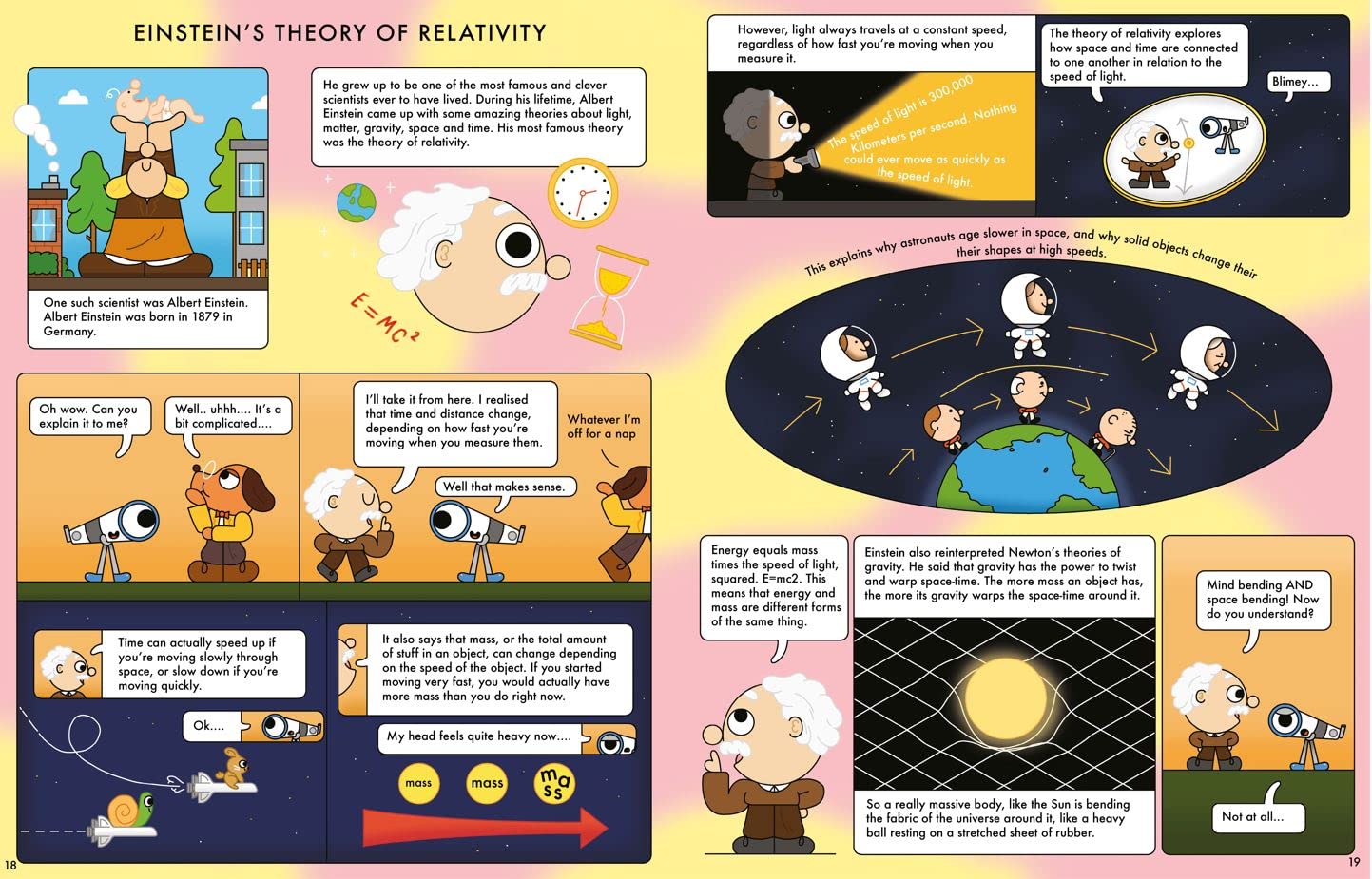
Sandra Neil Wallace’s exhilarating biography of Ursula Marvin transports readers to the snow and ice of Antarctica, where they get to ride along with this extraordinary woman as she fulfills childhood goals while changing the face of science and forging new opportunities for women. Wallace’s storytelling is fast-paced and evocative and infused with emotion, suspense, and scintillating details that will captivate readers no matter what their interests.
Nancy Carpenter’s beautiful mixed media illustrations allow children to see early influences and experiences that spurred Ursula Marvin to pursue geology and the study of meteorites in particular. Her images of Antarctica bring chills and thrills as Ursula sets up her tent, speeds over icy fields in the swirling snow on her snowmobile, and flops on the ground to inspect rocks up close. Carpenter also depicts Ursula’s victories and disappointments, giving children a well-rounded view of this remarkable woman. Rock hounds will be wowed by Carpenter’s drawings of moon rocks and meteorites.
With much to impart not only on the life of Ursula Marvin but on believing in yourself, overcoming disappointments, and chasing your goals with gusto, Rock Star: How Ursula Marvin Mapped Moon Rocks and Meteorites is a top pick for home, school, and public library collections.
Ages 4 – 8
Simon & Schuster/Paula Wiseman Books, 2025 | ISBN 978-1534493339
Sandra Neil Wallace writes about people who break barriers and change the world. She is the author of several award-winning books for children, including Love Is Loud: How Diane Nash Led the Civil Rights Movement, illustrated by Bryan Collier; Marjory Saves the Everglades: The Story of Marjory Stoneman Douglas, illustrated by Rebecca Gibbon; and Between the Lines: How Ernie Barnes Went from the Football Field to the Art Gallery, illustrated by Bryan Collier, which received the Orbis Pictus Book Award and was an ALA Notable Book. A former ESPN reporter and the first woman to host an NHL broadcast, she is the recipient of the Outstanding Women of New Hampshire Award and creates change as cofounder of The Daily Good, a nonprofit bringing twenty thousand free, culturally diverse foods to college students each year through its Global Foods Pantries. Visit Sandra at sandraneilwallace.com.
Nancy Carpenter is the acclaimed illustrator of Thomas Jefferson and the Mammoth Hunt, Queen Victoria’s Bathing Machine, Fannie in the Kitchen, and Loud Emily, among other books. Her works have garnered many honors, including two Christopher Awards and the Jane Addams Children’s Book Award. She lives in Brooklyn, New York. Visit her at nancycarpenter.website.
World Space Week Activity
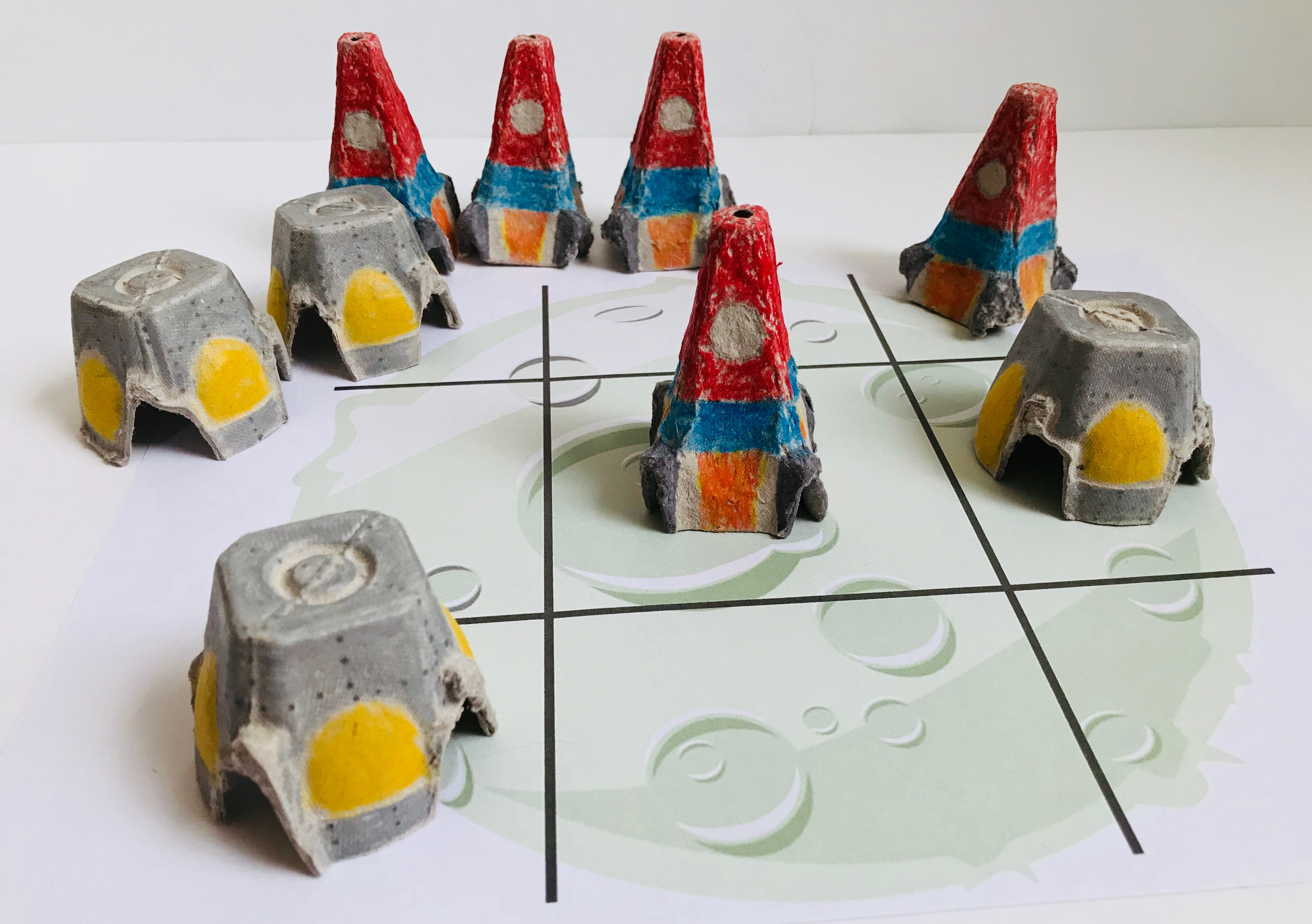
Out-of-this-World Tic-Tac-Toe Game
If you’re kids are fascinated by the moon, moon rocks, and meteors, they’ll enjoy making this tic-tac-toe game from simple materials you have at home!
Supplies
- Printable Moon Tic-Tac-Toe Game Board
- 2 cardboard egg cartons
- Heavy stock paper or regular printer paper
- Crayons
- Black or gray fine-tip marker
Directions
To Make the Rockets
- Cut the tall center cones from the egg carton
- Trim the bottoms of each form so they stand steadily, leaving the arched corners intact
- Pencil in a circular window on one side near the top of the cone
- Color the rocket body any colors you like, going around the window and stopping where the arched corners begin
- With the marker color the arched corners of the form to make legs
- On the cardboard between the legs, color flames for blast off
To Make the Capsule
- Cut the egg cups from an egg carton
- Color the sides silver, leaving the curved section uncolored. (If your egg cup has no pre-pressed curve on the sides of the cup, draw one on each side.)
- Color the curved section yellow to make windows
- With the marker, dot “rivets” across the capsule
Print the Moon Game Board and play!

You can purchase Rock Star: How Ursula Marvin Mapped Moon Rocks and Meteorites from these booksellers
Amazon | Barnes & Noble | Bookshop
Picture Book Review